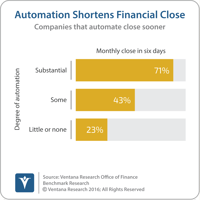
Robotic process automation (RPA) relies on programming or the application of analytical algorithms to execute the most appropriate action in an automated workflow. RPA enables business users to configure a “robot” (actually, computer software) to interact with applications or data sources to process a transaction, move or manipulate data, communicate with other digital systems and manage machine-to-machine and man-to-machine interactions. This technology is gaining increasing notice by finance...
Read More
Topics:
Operations,
automation,
close,
closing,
Continuous Accounting,
finance,
banking,
Robotic Process Automation,
Accounting
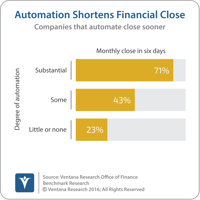
Kofax offers Kapow, robotic process automation (RPA) software used to acquire information from a range of sources without human intervention and without having to write code. These sources include websites, applications, unstructured documents, data stores and desktop spreadsheets. RPA software does repetitive, low-value work that otherwise may be performed by person. It saves time in these tasks, completing them sooner and freeing skilled individuals to concentrate on work that utilizes their...
Read More
Topics:
Office of Finance,
Operations,
close,
finance,
banking,
Digital Technology
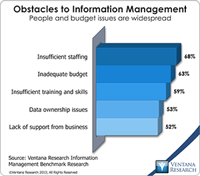
When applying information technology to drive better business performance, companies and the systems integrators that assist them often underestimate the importance of organizing data management around processes. For example, companies that do not execute their quote-to-cash cycle as an end-to-end process often experience a related set of issues in their sales, marketing, operations, accounting and finance functions that stem from entering the same data into multiple systems. The inability to...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Mobile,
Sales Performance,
Supply Chain Performance,
ERP,
Office of Finance,
Operations,
Management,
close,
closing,
computing,
end-to-end,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Data Management,
Information Applications,
Information Management,
CRM,
Data,
finance,
FPM
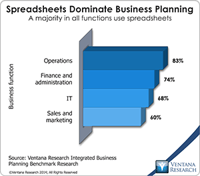
Anaplan, a provider of cloud-based business planning software for sales, operations, and finance and administration departments, recently implemented its new Winter ’14 Release for customers. This release builds on my colleagues analysis on their innovation in business modeling and planning in 2013. Anaplan’s primary objective is to give companies a workable alternative to spreadsheets for business planning. It is a field in which opportunity exists. Our benchmark research on this topic finds...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Performance Management,
Planning,
Predictive Analytics,
Sales Performance,
Supply Chain Performance,
Marketing,
Office of Finance,
Operations,
Reporting,
Budgeting,
Controller,
Operational Performance,
Business Analytics,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Financial Performance,
In-memory,
Workforce Performance,
CFO,
Sales Planning,
Financial Performance Management,
financial reporting,
FPM,
Integrated Business Planning
Organizations succeed through continuous planning to achieve high levels of performance. For most organizations planning is not an easy process to conduct. Planning software is typically designed for only a few people in the process, such as analysts, or organizations might use spreadsheets, which are not designed for business planning across an organization. Most technologies only allow you to examine the past and not plan for the future. For decades organizations have tried to focus planning...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Sales Performance,
Supply Chain Performance,
Mobile Technology,
Operations,
Operational Performance,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Cloudera,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Information Applications,
Workforce Performance,
Business Planning,
CFO,
finance,
Tidemark,
Workday