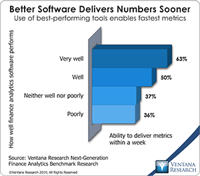
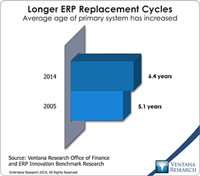
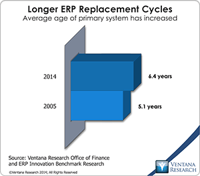
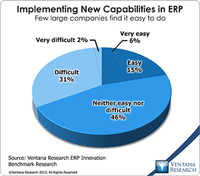
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
Mobile,
SaaS,
Sales,
Sales Performance,
Salesforce.com,
Supply Chain Performance,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
Kenandy,
PSA,
Sage Software,
Unit4,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Collaboration,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Workforce Performance,
CFO,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Workday,
HANA,
Plex,
Professional Services Automation
Like most vendors of on-premises ERP and financial management software, in moving to the cloud Oracle has focused on developing for existing and potential customers the option of multitenant software as a service (SaaS). (I’m using the term “ERP” in its most expansive sense, to include such systems employed by all types of companies for accounting and financial management rather than only systems that are used by manufacturing and distribution companies.) Oracle’s ERP Cloud Service includes ...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
Mobile,
SaaS,
Sales,
Salesforce.com,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
Kenandy,
PSA,
Sage Software,
Unit4,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Collaboration,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
CFO,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Workday,
HANA,
Plex,
Professional Services Automation
Like other vendors of cloud-based ERP software, NetSuite offers the key benefits of software as a service (SaaS): a smaller upfront investment, faster time to value and potentially lower operating costs. Beyond that NetSuite’s essential point of competitive differentiation from is broad functionality beyond financial management, including capabilities for customer relationship management (CRM), professional services automation (PSA) and human capital management (HCM). These components make it...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
Mobile,
SaaS,
Sales,
Social Media,
Customer Experience,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
communications,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
PSA,
Sage Software,
UI,
Unit4,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Financial Performance,
Workforce Performance,
CFO,
CRM,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Social,
Financial Performance Management,
FPM,
Plex,
Professional Services Automation,
Workday Collaboration
The keynote theme at this year’s Sapphire conference in Orlando was Simple. Top executives from SAP, a software company associated with complexity, stated and restated that its future direction is to simplify all aspects of its products and the ways customers interact with them and the company itself. SAP’s longstanding and commendable aspiration to thoroughness in its software will be giving way to an emphasis on elegance in its engineering. This objective is more than admirable – SAP’s future...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
Mobile,
SaaS,
Sales,
Salesforce.com,
Supply Chain Performance,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
Kenandy,
PSA,
Sage Software,
Unit4,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Collaboration,
Financial Performance,
CFO,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Workday,
HANA,
Plex,
Professional Services Automation
Epicor used its recent user group conference to explain its strategic direction and product roadmap. The company is the result of multiple mergers of business software corporations over the past 15 years; its target customers are midsize companies and midsize divisions of larger organizations. Its most significant products are Epicor (ERP software aimed mainly at manufacturing and distribution companies) and Activant Solutions (software for small and midsize retailers, including a point-of-sale...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
Mobile,
SaaS,
Sales,
Supply Chain Performance,
Customer Experience,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
communications,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
Epicor,
Sage Software,
UI,
Unit4,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Collaboration,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Workforce Performance,
CFO,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Workday,
Social,
Financial Performance Management,
FPM,
Plex
From my perspective, Infor’s strategy to accelerate revenue growth is to offer companies more innovation and a lower and more predictable cost of ownership than its rivals in the business software market; its products include the major categories of ERP, human resources and financial performance management. It aims to innovate by focusing on improving the user experience and to lower costs by redesigning its software architecture. The innovation stems from a fresh approach to designing...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
Mobile,
SaaS,
Sales,
Sales Performance,
Supply Chain Performance,
Customer Experience,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
Sage Software,
UI,
Unit4,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Information Management,
Workforce Performance,
CFO,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Workday,
Financial Performance Management,
FPM,
Plex
There’s a growing realization that the multitenant approach to the cloud isn’t the only option that companies should weigh in deciding between deploying software on-premises and in the cloud. That some people describe the multitenancy approach as “the real cloud” reflects the contentious nature of some technical debates, especially those that occur early in the evolution of a new technology. Multitenancy does have advantages that confer cost savings, and these have been important in the first...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
Mobile,
SaaS,
Sales,
Salesforce.com,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Planview,
Concur,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
PSA,
Sage Software,
Unit4,
Analytics,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Financial Performance,
Workforce Performance,
CFO,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Tagetik,
Workday,
Plex
Information technologists are fond of predictions in which the next big thing quickly and entirely renders the existing thing so completely obsolete that only troglodytes would cling to such outmoded technology. While this vision of IT progress may satisfy the egos of technologists, it rarely reflects reality. Mainframes didn’t disappear, for example. Although they long ago lost their dominant position, many remain key parts of corporate computing infrastructures. The IT landscape is a hybrid...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
SaaS,
Sales,
Salesforce.com,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
PSA,
Sage Software,
Unit4,
Analytics,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Financial Performance,
CFO,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Workday,
Plex,
Professional Services Automation
Convergence is the Microsoft Dynamics business software user group’s meeting. Dynamics’ core applications are mainly in the accounting and ERP category, descendants of products Microsoft acquired: Great Plains (now GP), Solomon (SL), Navision (NAV) and Damgaard’s Axapta (AX), to which Microsoft has added its own CRM application. It has been more than a decade since the acquisitions of Great Plains (which itself had already purchased Solomon Software), and Navision, Damgaard and the software...
Read More
Topics:
Microsoft,
SaaS,
Sales,
Sales Performance,
Salesforce.com,
ERP,
HCM,
Human Capital,
Office of Finance,
Consulting,
distribution,
Dynamics AX,
Dynamics GP,
Dynamics NAV Dynamics SL,
PSA,
Sage Software,
Unit4,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
CFO,
FinancialForce,
HR,
Infor,
Workday,
Plex,
Professional Services Automation