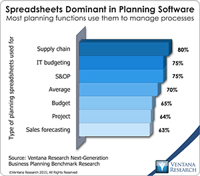
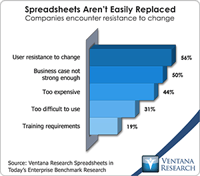
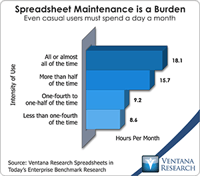
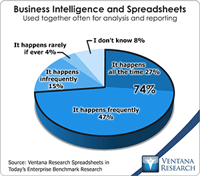
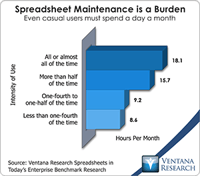
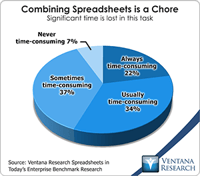
In our benchmark research at least half of participants that use spreadsheets to support a business process routinely say that these tools make it difficult for them to do their job. Yet spreadsheets continue to dominate in a range of business functions and processes. For example, our recent next-generation business planning research finds that this is the most common software used for performing 11 of the most common types of planning. At the heart of the problem is a disconnect between what...
Read More
Topics:
Planning,
Sales Performance,
ERP,
Forecast,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
closing,
dashboard,
enterprise spreadsheet,
Excel,
Customer Performance,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance,
Financial Performance,
Information Management,
Data,
Risk,
application,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management
Tagetik provides financial performance management software. One particularly useful aspect of its suite is the Collaborative Disclosure Management (CDM). CDM addresses an important need in finance departments, which routinely generate highly formatted documents that combine words and numbers. Often these documents are assembled by contributors outside of the finance department; human resources, facilities, legal and corporate groups are the most common. The data used in these reports almost...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Mobile,
ERP,
Human Capital Management,
Modeling,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
Budgeting,
close,
closing,
Consolidation,
Controller,
Finance Financial Applications Financial Close,
IFRS,
XBRL,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance,
Financial Performance,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
CFO,
compliance,
Data,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management,
financial reporting,
FPM,
GAAP,
Integrated Business Planning,
Profitability,
SEC Software
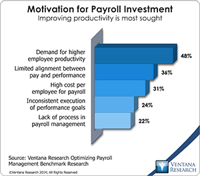
Our recently released benchmark research on optimizing payroll management assesses how organizations use payroll information, processes and technology. It finds that most of them still need to improve. Our analysis compared the forces motivating investment in payroll management systems to broader strategic drivers for human capital management (HCM) that I previously outlined and found substantial agreement. Three of the five leading factors – demand for higher employee productivity (48%),...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
HCM,
Office of Finance,
Employee Productivity,
Financial Performance,
Workforce Performance,
HR,
Talent Management,
Workforce Management,
benchmark,
Pay for Performance,
Payroll Management
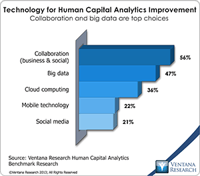
Learning is an integral component of human capital management, and a new generation of learning management systems advances learning in organizations around the world. These systems have evolved over the years from a classroom scheduling tool that facilitated instructor-led and classroom training into an array of enterprise applications that deliver and track various types of training. Recently new technologies, such as business analytics, cloud computing, social collaboration, and mobile...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Mobile,
Social Media,
HCM,
LMS,
Learning Management,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Intelligence,
Cloud Computing,
Collaboration,
Workforce Performance,
HR,
Training,
benchmark,
HR research
Our benchmark research on enterprise spreadsheets explores the pitfalls that await companies that use desktop spreadsheets such as Microsoft Excel in repetitive, collaborative enterprise-wide processes. Because people are so familiar with Excel and therefore are able to quickly transform their finance or business expertise into a workable spreadsheet for modeling, analysis and reporting, desktop spreadsheets became the default choice. Individuals and organizations resist giving up their...
Read More
Topics:
Sales Performance,
GRC,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
enterprise spreadsheet,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Collaboration,
Business Performance,
Cloud Computing,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Information Applications,
Information Management,
Workforce Performance,
Risk,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management
Oracle continues to enrich the capabilities of its Hyperion suite of applications that support the finance function, but I wonder if that will be enough to sustain its market share and new generation of expectations. At the recent Oracle OpenWorld these new features were on display, and spokespeople described how the company will be transitioning its software to cloud deployment. Our 2013 Financial Performance Management Value (FPM) Index rates Oracle Hyperion a Warm vendor in my analysis,...
Read More
Topics:
Big Data,
Mobile,
Planning,
Social Media,
ERP,
Human Capital Management,
Modeling,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
Budgeting,
close,
closing,
Consolidation,
Controller,
driver-based,
Finance Financial Applications Financial Close,
Hyperion,
IFRS,
Tax,
XBRL,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance,
CIO,
Cloud Computing,
Financial Performance,
In-memory,
Oracle,
CFO,
compliance,
Data,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management,
financial reporting,
FPM,
GAAP,
Integrated Business Planning,
Price Optimization,
Profitability,
SEC Software
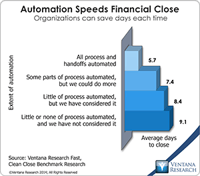
The spreadsheet is one of the five most important advances in business management over the last 50 years. It has changed all aspects of running an organization. It was the original “killer app” that made people go out and buy personal computers. So you see I’m enthusiastic about spreadsheets, but I realize they have limits that must be respected to work efficiently. One of the more important findings from our benchmark research Spreadsheets for Today’s Enterprise was about the time spent in...
Read More
Topics:
Sales Performance,
Supply Chain Performance,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
enterprise spreadsheet,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Information Applications,
Information Management,
Visualization,
Workforce Performance,
Risk,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management
I’ve been using spreadsheets for more than 30 years. I consider this technology tool among the five most important advances in business management of the 20th century. Spreadsheets have revolutionized many aspects of running an organization. Yet as enthusiastic as I am about them, I know the limits of desktop spreadsheets and the price we pay if we fail to respect those limits. The essential problem arises when people use desktop spreadsheets for purposes beyond what they were originally...
Read More
Topics:
Sales Performance,
Supply Chain Performance,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
enterprise spreadsheet,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC),
Information Applications,
Information Management,
Visualization,
Workforce Performance,
Risk,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management
Read More
Topics:
Sales Performance,
Supply Chain Performance,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
enterprise spreadsheet,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Performance,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Visualization,
Workforce Performance,
Risk,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management
I’ve been using electronic spreadsheets for more than 30 years. I consider this technology among the 20th century’s top five most important advances in business management. Spreadsheets have revolutionized every aspect of running any organization. A spreadsheet (specifically, VisiCalc) was the original “killer app” that made business people feel the necessity to buy a personal computer.
Read More
Topics:
Sales Performance,
Supply Chain Performance,
Office of Finance,
Reporting,
enterprise spreadsheet,
Operational Performance,
Analytics,
Business Analytics,
Business Intelligence,
Business Performance,
Customer & Contact Center,
Financial Performance,
Information Applications,
Information Management,
Visualization,
Workforce Performance,
Risk,
benchmark,
Financial Performance Management